Analog signals are an essential concept in both everyday life and the world of electronics. These signals represent continuous variations in physical quantities like voltage, temperature, or distance. A perfect example of an analog signal is the movement of the hands on an analog clock, where each small shift is a visible, uninterrupted change over time. Unlike digital signals that take discrete steps, analog signals are smooth and constant, resembling a sine wave. In this article, we will explore how analog signals work, their characteristics, and why they play a vital role in various applications.
What is Analog Signal
Analog Signal – Imagine the first friend tells the second friend that it takes five seconds for the second hand of his clock to move from 1 to 2, but the second friend sees nothing like this on his clock, which has no second hand.
Over time, the position of the second hand, minute hand, and hour hand on the clock changes, and this change is continuous. In an analog clock, you can observe every change in time (physical quantity), but you cannot see such changes in a digital clock.
So, from the above discussion, we can get a basic understanding of analog signals-
An analog signal is a type of signal where we can observe the continuous change in the physical quantity of different parameters (temperature, distance, etc.).
In electrical terms, an analog signal refers to the continuous change in voltage or current over time.
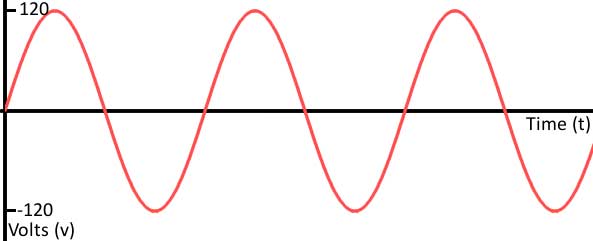
From the image, you can see how the value of voltage changes over time. This is an analog signal. An analog signal looks similar to a sine wave.
Analog signals can be described by two parameters-
- Amplitude, and
- Frequency.
An analog signal crosses a specific point after a fixed time, as seen in the case of the clock’s hands, and it continuously changes with time.
1. What is the difference between an analog signal and a digital signal?
Analog signals vary continuously over time and can represent a wide range of values, while digital signals take discrete steps and represent information using binary values. Analog signals are often represented by sine waves, whereas digital signals are represented by square waves.
2. What is an analog signal in a computer network?
In computer networks, analog signals are often used in telecommunications to carry data over long distances. For example, older telephone lines use analog signals to transmit voice, while modern systems convert those analog signals into digital data for more efficient transmission.
3. What is analog signal processing?
Analog signal processing refers to the manipulation or transformation of analog signals using analog circuits. This includes amplifying, filtering, and modulating signals for various purposes, such as sound or image processing in devices like radios and televisions.
4. Can you give an example of a digital signal?
A common example of a digital signal is the binary code used in computers. When you type on your keyboard, each character is converted into a digital signal (binary code), which the computer processes. Another example is the digital transmission of audio or video files over the internet.
5. What are analog and digital signals, and how are they used?
Analog signals represent continuous data, like sound waves, while digital signals represent data in discrete values (usually binary). Analog signals are used in older audio devices and radio transmissions, while digital signals are used in modern computers, smartphones, and digital audio systems for clearer, faster, and more efficient transmission.