What is a turbine: Turbines are critical machines used in various industries to convert kinetic, potential, and thermal energy into mechanical energy. From powering generators to driving engines in jet aircraft, turbines play a pivotal role in energy generation and mechanical operations. This article explores different types of turbines, including steam, gas, and water turbines, their functions, and the importance of their components in ensuring efficient energy transformation. We’ll dive into the working principles of impulse and reaction turbines, as well as the significance of components like nozzles, bearings, and governors in modern turbine systems.
What is a Turbine?
A turbine is a rotating machine that converts kinetic, potential, and thermal energy into mechanical energy.
Three types of fluids are used in it:
- Steam
- Gas
- Water
The turbine primarily acts as a prime mover that helps rotate the rotor of a generator and produce electricity. The turbine is the most critical mechanical machine, so it requires special care 🙂
Thermal and Gas Turbine
A turbine is operated using superheated high-pressure steam, which converts thermal energy into mechanical energy. Its usage is widespread in modern times. It primarily comes in three types:
- Impulse Turbine
- Reaction Turbine
- A type of turbine combining both
Imagine you are playing carrom. Some pieces can be knocked directly by striking them, while others require the help of the carrom board’s sides. When you can knock pieces directly, that’s like an impulse turbine, and when they bounce off the sides, that’s a reaction turbine.
To clarify further: if the fluid hits the turbine’s plates directly, those turbines are called impulse turbines. When the fluid strikes the plates in a more zigzag manner and generates mechanical energy, those are called reaction turbines.
There are also other types of turbines, classified based on stages, pressure, and steam conditions.
Steam Turbine
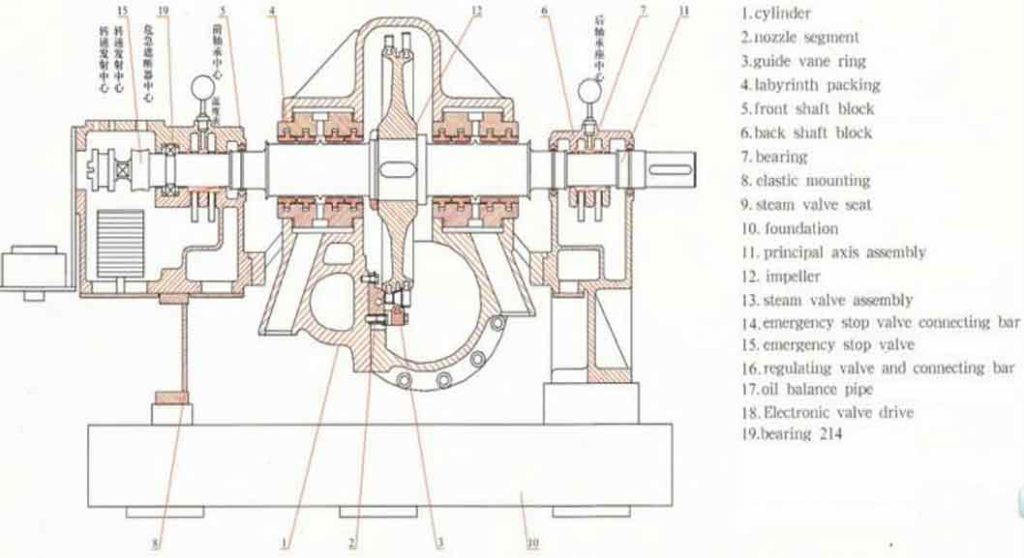
A steam turbine has a set of blades (called nozzles), a moving set (called rotor blades), a diaphragm, bearings (journal type), a governor lubrication system, input and output piping systems, all enclosed in a casing.
What does the nozzle do?
In short, it increases the velocity of the fluid. The diaphragm holds it in place.
Bearings
Bearings are components that are used in all rotating machinery, such as wheels, fans, etc.
Functions of Bearings:
- To carry the load.
- To help the shaft rotate and hold it in place.
- To reduce friction.
Governor
It controls the steam flow in the turbine to regulate power and speed.
Overspeed Trip Mechanism
It protects the turbine from damage in case of overspeed.
Coupling
It connects to the driven machine.
How It Works
- High-pressure, high-temperature steam jets into the nozzle.
- The nozzle increases the fluid’s velocity, striking the turbine blades, which then cause the shaft to rotate.
The working cycle is called the Rankine cycle. It includes several more steps.
Gas Turbine
A rotating engine extracts power from the flow of combustion gas. When we visit an airport, we see jet planes powered by large engines. These engines are usually driven by turbofans, which are examples of gas turbines.
In many modern industries, gas power plants are used. They typically require less space, have shorter start-up times, don’t need water, have low weight, simple construction, and no condenser, making them widely used.
What is a turbine and example?
A turbine is a rotating device that converts kinetic energy from fluids such as wind, water, steam, or gas into mechanical energy. An example of a turbine is a wind turbine, which converts wind energy into electrical energy, or a steam turbine used in power plants to generate electricity from steam.
What is the principle of a turbine?
The principle of a turbine is based on converting the kinetic or thermal energy of a moving fluid into mechanical energy by rotating blades attached to a rotor. As the fluid passes through the turbine, it imparts force to the blades, causing rotation and thus generating mechanical or electrical energy.
What are the three types of turbines?
The three primary types of turbines are:
Steam Turbine – Converts steam energy into mechanical energy.
Gas Turbine – Uses hot combustion gases to produce mechanical energy.
Water Turbine – Utilizes flowing water to generate mechanical power, commonly seen in hydroelectric plants.
Why are turbines used?
Turbines are used to convert energy from natural or mechanical sources (such as wind, steam, water, or gas) into mechanical power, which is then often converted into electrical power. They are essential in generating electricity, powering engines, and driving industrial machinery.
What is turbine efficiency?
Turbine efficiency refers to how effectively a turbine converts the energy of a fluid (like steam, wind, or water) into useful mechanical energy. Higher efficiency means more energy is converted with less waste, making the turbine more economical and environmentally friendly.
Which type of turbine is mostly used?
The most commonly used turbine depends on the application. For electricity generation, steam turbines are widely used in thermal power plants, while wind turbines are commonly used in renewable energy setups. Water turbines are prevalent in hydroelectric power plants.
What are the applications of turbines?
Turbines are used in various fields such as:
Power generation (steam, gas, wind, and hydro turbines)
Aircraft engines (gas turbines)
Industrial machinery (mechanical energy from turbines)
Renewable energy sources (wind and hydro turbines)