As we know, the transformer is the heart of a power system. We can’t imagine Generation/Transmission/Distribution power system beyond a transformer. Today, I am going to discuss phase shifting transformer in a nutshell. Let’s discuss.
What is phase shifting transformer?
We can identify a tree by its fruit. Similarly, the “phase shifting” term highlights its function. Actually, phase shifting transformer is a special type transformer that delivers a phase-shifted output power with a desired angle from the input power. But the mentioning fact is, here the phase of the output quantity can be continuously varied keeping magnitude constant.
Construction of phase shifting transformer
Now, let’s see the construction of phase shifting transformer within a few words. Because you will not be able to realize the working principle without acquiring the basic knowledge of construction. You may be surprised to hear that, the construction of a shifting transformer is similar to the induction motor.
How it is similar to induction motor?
It mainly consists of two parts:
- a stator winding kept at stationary;
- a rotor winding that can be movable;
- Firstly, The stator of a phase shift transformer is wound with single or three-phase windings as seen in induction motors. The stator windings are kept on the stator slots of laminated silicon steel to reduce iron losses.
- As We know that, a device can rotate while producing rotating magnetic field. Single-phase induction motors can’t produce rotating magnetic field. So, they are not self-starting motors.
- The single-phase winding of a phase shift transformer split into two windings as shown below.
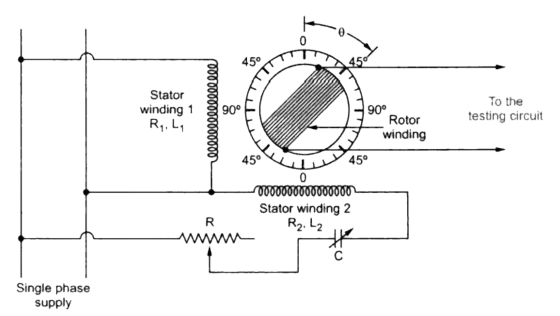
Working principle
Basically, the manufacturer’s design phase shift transformer with quadrature winding arrangement. Now, I want to make a clear concept about quadrature winding arrangement by the following picture:
- Suppose, you throw a stone in a lake. Then the water molecules will displace after throwing this stone. In this case, when we give single phase supply to the two-phase stator winding displaced at 90°. Here you can compare the power supply with the motion of stone. On the other side, displacement of water molecule and stator winding is similar to each other.
- It produces a uniform rotating magnetic field and links with the rotor conductors.
- By varying resistance and capacitance, required phase splitting is achieved to produce rotor induced emf according to following equation:
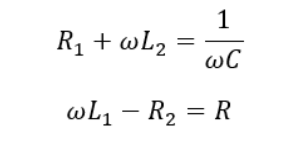
- we can obtain a required variable phase shift from the rotor output according to the rotor displacement.
- A question may hit upon your mind that, if we shift the phase what about the magnitude value of emf?
- It can be seen that the rotor winding is arranged in such a way that change in phase shift doesn’t affect the magnitude of the induced emf.
Advantages of phase shifting transformer
- Enhance the reliability and efficiency of the power grids.
- controlling active or real power flowing through a multi-network power system.
- Controlling the load the current by adding circulating current.
- Balancing loads.
- To control power demand levels.
Read more articles
What is the Function of Silica Gel in a Transformer?
Transformer Insulation Test | Briefing Tan Delta Test in a nutshell


