Today’s topic is the microwave oven uses and functions. The use of a microwave oven is very common now. Let’s unwind everything about it today.
Microwave Ovens are like Aladdin’s magic lamp. They cook your food without any external heat. Another perspective of a microwave oven is if it is hazardous to human health due to its electromagnetic radiation.
- What is a microwave oven?
- The Introduction of a Microwave Oven.
- How do Microwave Ovens operate?
- How Electromagnetic Waves Help in Cooking Food?
- The Workable Structure of a Microwave Oven.
- How does a Microwave Oven Cook the Food evenly?
- Are Microwaves the only Electromagnetic Waves capable of Heating Food?
- Microwave Oven Uses and Functions.
- Why is heating with a microwave oven superior to conventional heating methods?
This article will try to answer these questions.
What is a Microwave Oven?

Microwave ovens are small boxes. These are not any simple boxes made of steel or plastic material. These ovens produce well-cooked food for us. How do they do it?
Actually, microwave ovens provide high-frequency microwaves to the food particles. We know that all our food elements have water inside them. The microwave produces kinetic energy in the water molecules. This eventually heats the food.
We will learn about this matter in-depth throughout this article.
The Introduction of a Microwave Oven

So let’s dive right into it. It may amaze you! The invention of the microwave oven was accidental.
Scientist Percy Spencer was performing experiments on a device called a magnetron.
What is a Magnetron?
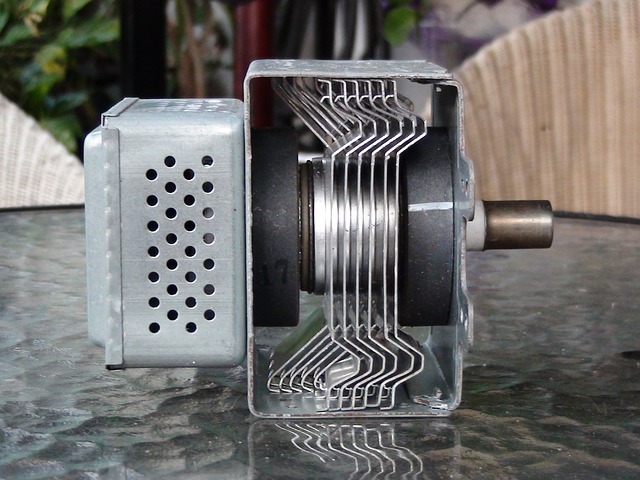

Magnetrons generate powerful microwave radiation.
During the experiment, scientist Percy made an observation that the candy bar in his pocket was gradually melting. That’s when he got the whole idea to explore the applications of microwaves in cooking food.
This little phenomenon has today got us where we are now.
The conclusion from this experiment was that a high-powered traveling microwave has the capability of heating food.
How do Microwave Ovens Operate?
Now, a question arises,
What was in the microwave that melted the candy bar?
What are Microwaves?
Microwaves are electromagnetic waves in a particular spectrum. Microwaves have oscillating electric and magnetic fields much like any other electromagnetic wave.
Now, if you track the amplitude of the wave in a specific area, you can observe this oscillation in the chocolate melting accident case. This oscillating electric field component of the electromagnetic wave is responsible for cooking the food.
How Electromagnetic Waves Help in Cooking Food?
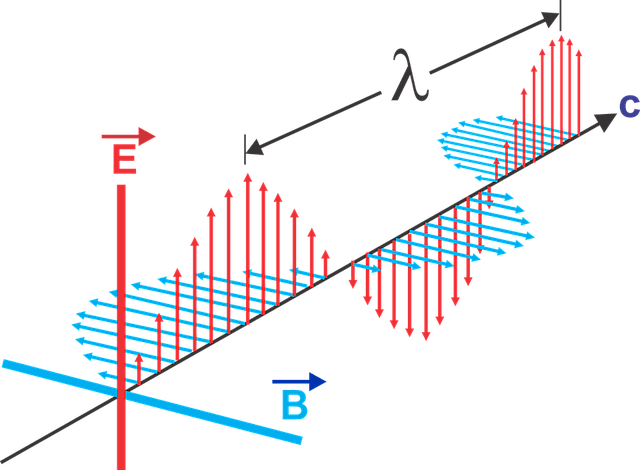
Now, let’s see how the oscillating electric fields cook food.
What is a dipole:
- Most of the food that we consume has water in it.
- Water is a polar molecule. The hydrogen atoms of the water molecule stay at an angle of 104 degrees from each other.
- Moreover, both the hydrogen and oxygen atoms have charges.
- This makes the water molecule behave like a dipole.
When we apply an electric field to the water molecule it starts to rotate due to the torque of the dipole. In electromagnetic waves, the electric field oscillates continually. The water molecules also keep on oscillating. Due to this oscillating rotation, the molecules rub against each other. This produces friction and heat in the food.
The Workable Structure of a Microwave Oven
Now, let’s look at how to convert this heat generation concept. We need to convert it into a workable product to use the energy of the electromagnetic wave efficiently. We need to reuse it several times. An efficient way of achieving this is to reflect it. We can achieve this by confining it to a particular area. The best way of making this reflector is with the help of metal.
How Metallic Reflector Helps
- The metallic surface causes the microwave to reflect from its surface.
- If you keep one more reflector at the source side the reflection will keep on continuing.
- This way we will be able to trap the energy of electromagnetic radiation within a volume.
Resonance Cavity
However, the most efficient way of trapping electromagnetic wave energy is by use of a technique by the name resonance cavity.
This method also increases the intensity of electromagnetic waves. Let’s understand the concept of resonance cavity using a simple approach of standing waves.
What is a Standing Wave?
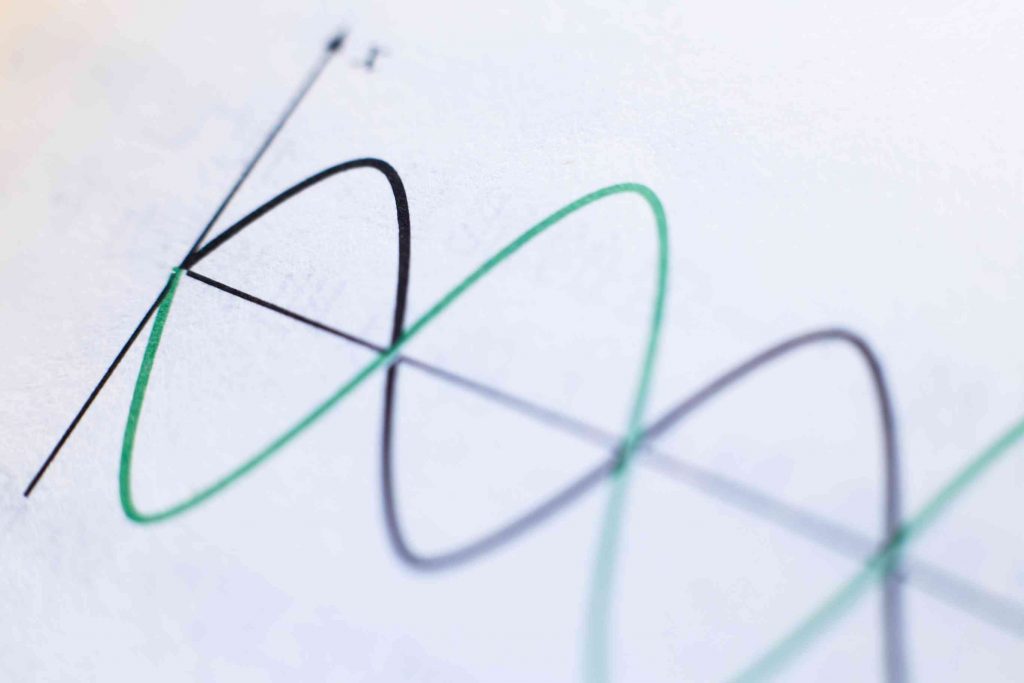
A standing wave is a stationary wave that fluctuates in time. It does not propagate in space. Its formation takes place due to the superimposition between two waves having the same amplitude and the same frequency moving in opposite directions.
How does a Microwave Oven Cook the Food evenly?
Now, clearly observe the standing wave. You can see some points of the standing wave are at high energy intensity and some other points are at zero intensity. Due to this, there would be many spots in a microwave. Some cold and others hot.
For example: use cheese. Keep a shredded cheese inside your microwave oven for one minute. What do you see after one minute? You can see the cheese surface with a few hot spots. The presence of such hot spots causes a microwave to cook food unevenly.
What is its reason?
We use the cavity resonance technique to trap the microwaves more efficiently. It leads to the creation of cold and hot spots.
What is the solution?
To overcome this problem nowadays a microwave consists of a rotating plate. This plate helps to cook the food evenly. So, the component responsible for producing microwaves is what we know as a magnetron. Additionally, a magnetron emits microwaves in all directions. Now we need to confine the wave to propagate in one dimension. There is an attachment of the magnetron to the waveguide. From the waveguide, the waves come into the cooking chamber to heat food.
Are Microwaves the only Electromagnetic Waves capable of Heating Food?
Is there any other way to accomplish the same result? Do any other electromagnetic waves have the same capability to heat food?
There are. But, they come with certain limitations.
The limitations:
- Waves with long wavelengths can easily pass through our food.
- As a result, they won’t be able to transfer much energy to it.
- Additionally, to get a standing wave, there is the need for large devices.
- Moreover, absorption of shorter wavelength waves takes place more rapidly on the outer surface of the food.
- So they do not penetrate far enough down to cook it evenly.
Now, if we want to cook deeply we have to switch to a very high power source. So, the source should be unfeasible. In the microwave range, the suitable frequency for all practical purposes and which does not require a license is 2.45 gigahertz.
Microwave Oven Uses and Functions

The human skin is highly responsive to microwaves by a magnetron. The direct exposure of the powerful microwaves of an oven is hazardous to humans. There is no need to worry in this case. The electromagnetic radiation by a microwave oven always stays within it. It will never leave the chamber. So there is no point in worrying about the microwave oven uses and functions. Now, if you think about the microwave oven uses and functions, it causes no health issues. Moreover, it is our daily driver. From our breakfast till dinner, it serves us effortlessly. So, the use of a microwave oven is increasing day by day. It is in use at homes, restaurants, public gatherings, etc.
Why is heating with a microwave oven superior to conventional heating methods?
The reasons:
- Microwaves can penetrate the food. As a result, the heat reaches the insides of the food.
- Moreover, it cooks food faster than other conventional methods.
- Conventional methods cook food from the outside. This is because the heat energy has to travel from outside to inside.
- But this method can be useful on some occasions when you need food with a crisp surface and a soft interior or baking.
- Modern microwave ovens come with a conventional option for baking purposes.
Conclusion
I hope you enjoyed my ultimate guide to microwave oven uses and functions.
Now I’d like to hear from you: do you use a microwave oven? Do you like the conventional oven or microwave oven?
Either way, let me know by leaving a quick comment below.
Read More Exciting Articles