How does Computer Memory work? This question bugs a lot of tech geeks nowadays. How about learning it in a fun manner today?
I often wonder if my memory is like a computer. But in reality, human brains and computer memory are not the same things at all. They work completely differently and for different purposes. Where human memory struggles to remember a name, to remember someone’s face, or to remember today’s date, computer memory is becoming more and more perfect day by day. Our question today is, how does a computer have this extraordinary memory? How does computer memory work? So let’s get to know everything in detail.
What is Memory?
In order to learn how does computer memory work, you first have to know what memory is. The basic purpose of any memory (be it human memory or computer memory) is to store some information for a certain period of time. The most interesting thing is that human memory is more adept at forgetting information than remembering any information. In fact, this is the weakest part of our brains. If you don’t pay attention to something, no one can save you from forgetting it. So, because of our inability to easily forget something, we pay close attention to something important. Forgetting means cleaning up an old trash can and getting it ready to fill up again.
Computers never remember or forget things the way humans do. The computer works in binary. Whether they know it or not, once a computer learns something, it will never forget it without a catastrophic crash. But we humans are a little different. We can recognize something (“I think I saw you somewhere before”) or we think we know it (“I first learned the English word ‘pair’ when I was in school”) and we need to gather information without any need for it then.
Unlike computers, people forget something, they think again, forget again, think again and repeat. Honestly, human memory seems a lot like magic to me. But the truth is, a pen drive worth 5 Dollars is better at remembering than our brain.
Two Types of Memory
One of the similarities between human and computer memory is that they both have two types of memory. Human memory is mainly divided into two parts, one is short term memory (which you have recently seen, heard, or imagined in the brain) and the other is long term memory (which we have learned, or We have experiences from our lives, and this is why we remember them better).
In this way, the computer also has two types of memory. It has a kind of built-in memory we know as internal memory. The preparation of it takes place by a silicon chip. This memory enables a computer to store and retrieve data much faster. So the use of it to complete the current processes of the computer.
Internal Memory
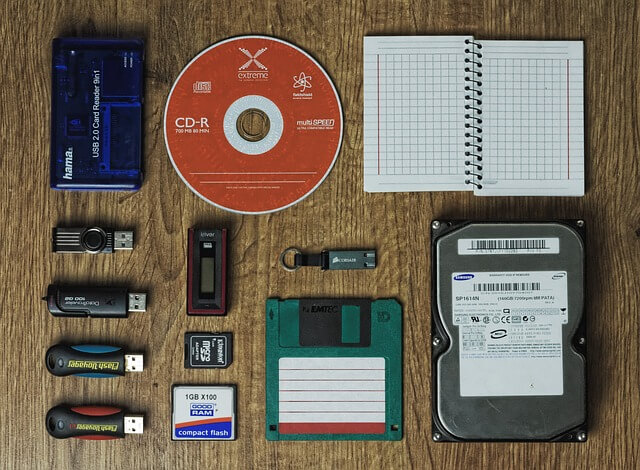
Normally, a computer’s internal memory becomes volatile (that is, it evaporates rapidly). That is, all the information we store in a computer disappears as soon as we switch it off. Again, this requires another type of computer memory, which we know as auxiliary memory or storage. This memory can store any information even when the computer is off. A hard drive or flash storage on a normal PC or laptop is what is basically an auxiliary memory. Auxiliary memory is also a reference for external memory. Because the hard drive is a separate machine that we connect to the computer via a cable. Moreover, with today’s modern computers, we can very easily find plug-in memory, such as a USB flash memory stick or SD memory card, portable hard drive, CD or DVD ROM, etc.

Virtual Memory
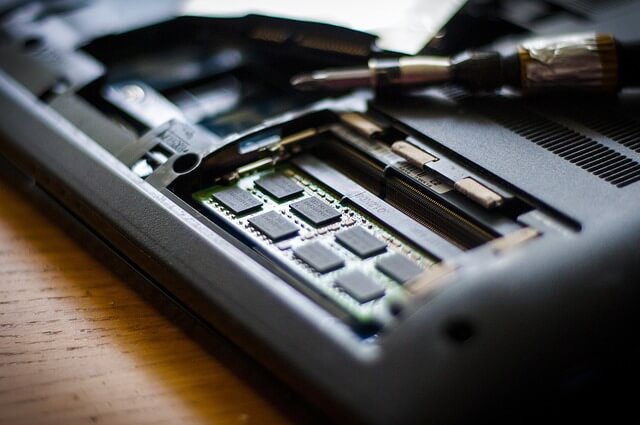
The main memory of the computer, however, is much less, usually from 512 MB to 8 GB (modern computers have more memory). The more main memory the computer has, the more information the computer will be able to process and work faster. If the computer needs to store more data than its main memory, it stores it in some free space on the hard drive, and this is what we call virtual memory.
You may have some idea about the Virtual Memory option on Windows computers. How about we try and find out the truth about it today. If you notice that your hard drive is busy reading and writing a lot of data most of the time, your computer is using the hard drive as virtual memory. Virtual memory is theoretically used to speed up computer performance. But in real life, it can slow down your computer performance. Because auxiliary memory can never be as fast as main memory. So if the size of your computer’s main memory means the size of RAM is less, it would be best to upgrade. Now, you should keep some things in mind, for example, why is my PC slow? Find out exactly which version of the PC can work in favor of your computer performance.
Internal memory: RAM and ROM
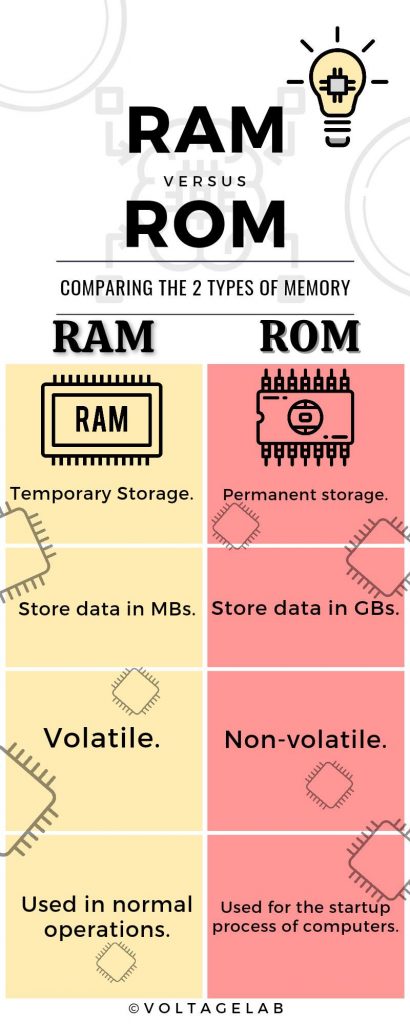
Computer internal memory chips are of two main types, one known as RAM (Random Access Memory) and the other known as ROM (Read Only Memory). The RAM chip can remember any information as long as the computer is on power. So they store the data in the short term. ROM chips, on the other hand, can store data even when the computer is not on. When we prepare ROM in the factory, we can program it and embed the information in it beforehand.
So, what do you understand? Computers have two types of memory chips. One can remember information temporarily, that is, as long as the computer is on, that is RAM. Furthermore, another is a permanent way to remember any information, even if the computer is off, that is ROM.
What is Random Access?
This is basically a confusing question. RAM means random access. Because it helps the computer to read and write data quickly. Again, at the same time, it is possible to access data anywhere. Computer hard drives are also random access devices. Because at the same time it is possible to access any data from any point of the hard drive.

However, not all types of computer memory are randomly accessible. For example, a tape drive by attaching a plastic strap and a magnet that reads data from it. Now if the computer wants to access information at a certain point from this tape, the reel of the tape will start moving back and forth. It will keep happening just as long as it can not reach that particular point. Suppose, the reel of the tape is now at the beginning and the computer wants to access the data at the very last point. So it will take a long time to access that data. The reel will turn and reach that point and then the data will be accessible. As a result, this is what modern researchers term sequential access.
Types of RAM
RAM is mainly of two types, one is DRAM (Dynamic RAM) and the other is SRAM (Static RAM). DRAM is less expensive than SRAM. Again, it tends to be of higher density (meaning it can hold more data in smaller sizes). So, we can use DRAM as internal memory. Most of the time, we use it on PC, gaming consoles.
ERAM, on the other hand, costs a lot more and is much faster with less power loss. But its data capacity is much lower. ERAM is specifically called cache memory. The use of it is especially in portable gadgets such as cellphones. Here, there is more requirement for speed to save power.
DRAM and ERAM do basically the same thing. We can make them using slightly different electronic components while making them. Both of these two types of RAM can forget information. But we need to turn off or power off the computer in order to refresh the memory of DRAM. On the other hand, ERAM does not refresh the memory in this way. DRAM can hold more data in a smaller size because it uses a capacitor and a transistor to store a bit. But to save a bit in ERAM, we need some capacitors and a transistor.
ROM
Computer memory has the same variety of ROMs as RAM. Again, it is a bit of a random thing here, because not all ROMs have read-only memory. Flash memory of your phone or camera, USB pen drive, etc. Are nothing but a kind of ROM. Because it has the ability to remember the data even after we power it off. Technically speaking, flash memory is EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable ROM) type ROM. This means that in order to store and delete any information, an electric current needs to flow through it.
In fact, you can not store your smartphone, modem, or router’s framework in the ROM. You can store it in its flash memory. So that you can upgrade it later. ROMs are much slower than RAM and don’t have as much read and write capability as RAM.
How Computer Memory Stores Data in Binary?

Computer memory: stores any photo, video, music, or any computer information in the form of numbers. Again, this is why we call these computers “digital computers”. We humans like to work using decimal numbers (10 numbers from 0 to 9). But computers work using completely different number systems. They use a binary number system. Binary has only two numbers, Zero (0) and One (1). It requires multiple numbers to write a decimal number. Binary digits are called bits, that is, one is zero or one is one bit. Eight bits together is called a byte.
A big reason why we humans like to use decimal numbers is that we have 10 fingers. But a computer does not have 10 fingers. Instead of fingers, the computer memory contains millions of electronic switches, which we know as transistors. Transistors can store any binary number when electric current flows through it. When we switch on a transistor it saves the number (1) and when we turn it off it saves the number (0).
Conclusion:
So this was the secret of computer memory and its extraordinary memory. I hope you all understood how does computer memory work? Hopefully, I was able to present this whole issue about how does computer memory work, to you very easily, and today’s post was a source of information. If you like the post, be sure to share, comment and maintain your support in this way.
Check More Articles