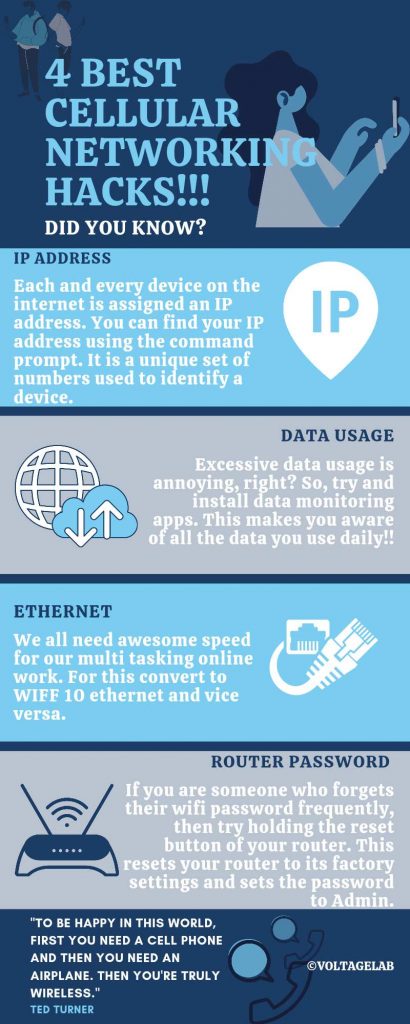
Cellular network design site selection and frequency planning are two very interesting topics to talk about. Today we will learn how different operators design their cellular networks. First, we need to know what a “cellular network” is.
Cellular Network

The term cellular network comes from cells. Now let us know what a cell is? Suppose, I set up a mobile company. Now for that, I will be allotted bandwidth by the government (BTRC). Cellular network design site selection and frequency planning are interrelated with bandwidth.
Bandwidth is the radio channel capacity. Again, the channel is the path of data circulation. Moreover, many radio channels combine together to form a cell. Furthermore, the coverage of the cell is the cellular network.
A cell is made up of an antenna and a small office. Small offices with antennas are called base stations. A very small area or cell network coverage is provided by a base station.
Each base station is controlled by a mobile switching center, where call connection, call information recording, billing system, etc. are controlled in a computerized manner. Cell sizes usually range from 1 mile to 12 miles, depending on the density of the population.
Bandwidth and an Analogy
Suppose, my bandwidth is 20 MHz. Now, I have to arrange my channels in such a way that it does not go beyond this capacity. Well, then it’s time for design.

Now, after I set up radio channels in 50 areas, I saw that my allotted bandwidth was over. What happens now? So what will happen to the rest of the poor customers? Will they not get any network? So, there is nothing to worry about.
There must be a solution. You will then need to reuse the channel. That is, reuse the frequency channels that you used in the area up to 1-50. Otherwise, your company will be shut down by the government. This method is called “Frequency Reuse”.
Cellular Network and Coverage System
One area consists of one cell. Again, for this, you have to design a cellular network. Now, this cell size is considered hexagonal.
First of all, the area coverage system should be such that the cellular network cells in one area do not overlap or interfere with the cells in another area. If I consider circles as hexagons instead of hexagons, then many circles can create overlapping side by side.
In fact, the biggest thing is that you can’t leave gaps in the cells while mapping your network. Otherwise, it can show the signal to be nil in a specific part of the area for such a design. Because, if you draw a lot of circles one after another, up and down, there will be a gap.
So, hexagons are considered without considering circles. Now, some may say, why? I can draw many triangles or quadrilaterals without leaving a gap. Why do we only consider hexagons? In fact, how or what pattern the antenna of the mobile tower radiates the signal, is also considered.
Usually, the microwave sector antennas of the mobile tower give signal radiation in a circular pattern. So, in this case, you have to consider the geometric field of the galaxy while designing. So, in this case, you have to consider a geometric shape that is the circle. But, I have already explained that the circle is not possible. So, a hexagon is considered as a geometric figure close to a circle. This is how cellular networks are designed.
Check More Articles