Capacitors are fundamental components in both electrical and electronics systems, widely used in circuits for storing and regulating electrical charge. From paper capacitors to variable capacitors, each type plays a specific role based on its material composition and function. Understanding the characteristics and applications of these capacitors is essential for anyone involved in electronics, as they are key to the proper functioning of various circuits, including power supplies, amplifiers, and radio tuners. In this article, we will explore the different types of capacitors, their structure, working principles, and typical use cases.
A capacitor is essentially an electrical component made up of two conductive plates with a dielectric insulating material between them. It is a widely used component.
What is a Capacitor or Holder?
Simply put, a capacitor or holder is somewhat like a rechargeable battery, but its capacity to store charge is much smaller.
In textbook language, “It is an electrical device made up of two conductive plates with a dielectric insulating material between them.”
Symbol, Unit, and Charge:
Symbol of a Capacitor:
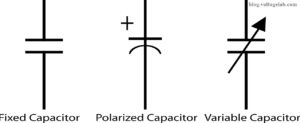
The SI unit of a capacitor is farad (F). Since farads are quite large, they are commonly expressed as microfarads (µF), picofarads (PF), or nanofarads (nF).
Capacitance:
The property of a capacitor to store electrical energy or charge is called capacitance. When there is a potential difference between the plates in a capacitor, it is in a charged state, and when there is no potential difference, it is in a discharged state.
Formula:
Capacitance = Charge / Potential Difference
In other words, C = Q / V
Where,
C = Capacitance,
Q = Charge,
V = Potential Difference,
Types:
Electrolytic Capacitor
This capacitor has both positive and negative polarity and is a polarized capacitor. Since electrolytes are used in its construction, it is called an electrolytic capacitor. It is only used in circuits where DC or pulsating DC flows. Electrolytic capacitors are used for storing a large amount of charge in a small space.
This is a high-capacitance capacitor that is most commonly used. While it is used in filter bypass circuits in radios, it cannot be used in AC circuits.
Features of an Electrolytic Capacitor:
- It is a type of polarized capacitor.
- Its two plates are marked as positive and negative electrodes.
- It is generally used in DC circuits.
- The capacitance of such capacitors is typically 1 microfarad or more.
- They are very small in size.

Construction and Working Principle of an Electrolytic Capacitor:
Two aluminum (AL) plates are placed between an appropriate electrolyte, i.e., an electrolyte or conductive liquid (usually a mixture of ammonia, boric acid, and water). When direct current (DC) is applied, a thin layer of aluminum oxide forms on the aluminum plate connected to the positive terminal of the DC source. This layer is non-conductive (insulator) and acts as the dielectric between the two plates. To maintain this dielectric layer, the plate connected to the DC source is marked with a positive (+) symbol.
This assembly is placed inside an aluminum capsule, with an aluminum terminal connected to the capacitor’s negative terminal. One plate of the electrolytic capacitor is used as the positive terminal, and the other as the negative terminal. Care must be taken during circuit connection to ensure the positive terminal is connected to the circuit’s positive terminal, or else the oxide layer could be damaged, causing the capacitor to fail.
Types of Electrolytic Capacitors:
There are primarily two types of electrolytic capacitors:
- Wet type
- Dry type
Wet Type: This type of capacitor has one aluminum electrode and the other is an electrolytic solution, typically made from a mixture of ammonia, boric acid, and water.
Dry Type: In this type, both plates are made from long strips of aluminum and separated by a special paper soaked in an electrolyte. They are then tightly wound together and secured.
Non-Electrolytic Capacitor:
Non-polarized capacitors that do not have positive and negative polarity markers are called non-electrolytic capacitors. These are made by placing an insulating medium, such as paper, mica, ceramic, or polyester, between two metal plates. They are enclosed in plastic or metal capsules, with the insulating medium acting as the dielectric. The name of the capacitor depends on the dielectric material used, such as paper capacitors, ceramic capacitors, mica capacitors, polyester capacitors, and styroflex capacitors. These capacitors typically have capacitance values in the range of a few hundred picofarads.
Paper Capacitor
This is a widely used capacitor. It uses paper as the dielectric, hence the name ‘paper capacitor’.
Paper capacitors are used in both high and low voltage circuits. They are generally used as coupling and bypass capacitors in power supplies and amplifiers.
Paper Capacitor
This is a widely used capacitor. Paper is used as the dielectric material in this capacitor, hence it is called a paper capacitor.
Paper capacitors are used in both high and low voltage circuits. They are commonly used as coupling and bypass capacitors in power supplies and amplifiers.
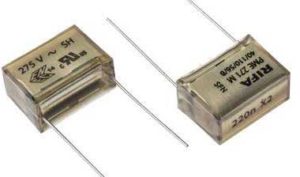
Ceramic Capacitor / Non-Electrolytic Capacitor
Ceramic is used as the dielectric in ceramic capacitors. The dielectric constant of ceramic is very high, ensuring the stability of the capacitor despite temperature and voltage changes. Their values typically range from 1 picofarad to 105 picofarads, and their working voltage is limited to 500 volts. These capacitors are particularly suitable for shortwave circuits. They are used in tuning circuits, bypass circuits, and for coupling. Ceramic capacitors have very low capacitance.

Mica Capacitor
Mica is used as the dielectric material in these capacitors. Usually, their value and voltage rating are written on them. However, in some cases, a color code like that used for resistors is provided to determine their value. They are typically used in high-frequency circuits such as RF (Radio Frequency) circuits in receivers and transmitters.

Polyester Capacitor
This type of capacitor uses polyester foil as the dielectric. The outer side is covered with special insulation and a waterproof lacquer. Their capacitance values range from 1nF to 15uF, and their working voltage is limited to 500 volts. These capacitors are stable, moisture-resistant, compact, and inexpensive, making them widely used in various circuits, especially in coupling and bypass circuits.

Variable Capacitor
The capacitance of this type of capacitor can be adjusted as needed. These capacitors consist of multiple moving plates. By adjusting the position of the plates, the capacitance can be increased or decreased. Variable capacitors are commonly used in radio tuning circuits.

Styroflex Capacitor
Styroflex is a small, transparent capacitor. It has very low loss and excellent frequency characteristics. Their working voltage ranges from 125 volts to 250 volts. Their capacitance value, working voltage, and tolerance are usually printed on the body. Styroflex capacitors are often used in tuning oscillators and frequency-determining circuits.
Mica Tuned Capacitor
Also known as a trimmer capacitor, this type has very low capacitance, usually between 4 picofarads and 70 picofarads. The capacitance is adjustable but offers only minor variations. They are used in radio tuning circuits.
Air-Spaced Capacitor
An air-spaced capacitor is a type of non-electrolytic capacitor. In these capacitors, air is used as the dielectric between the plates. Capacitors that use air as the dielectric are called air-spaced capacitors. Their capacitance value is quite low, typically under 0.01 uf. Air-tuned capacitors are used for precise radio tuning.
Air-Spaced Capacitor
Air-spaced capacitors consist of multiple metal plates arranged in two rows with a small gap between them. One row of plates remains stationary, called the stator plates. The other row of plates, called rotor plates, can move in and out of the gaps between the stator plates. The rotor plates are connected to a shaft for rotation. The air between the stator and rotor plates acts as the dielectric, keeping them apart.
Frequently Asked Questions About Capacitors:
Capacitors are a very important component in both electrical and electronic systems. Capacitors are needed for most electronic projects.
Here are some important questions related to capacitors that might come up in job interviews or written exams:
- What is a Capacitor?
The term “capacitor” refers to a device that stores electrical charge for a brief period.
- What is the role of a capacitor in a circuit?
A capacitor holds charge for a brief period. It can be compared to a battery, though a battery holds charge for a much longer duration. Capacitors are also used for filtering purposes.
- What type of capacitor should be used in a power supply?
A high-quality capacitor should be used in power supplies. Since the components rely on the power supply for operation, it is essential to use a good quality capacitor in the power supply.