The sun provides us with both light and heat, essential for life on Earth. Beyond these basic benefits, solar energy can also be harnessed to generate electricity, thanks to solar cells. A solar cell, also known as a photovoltaic (PV) cell, converts sunlight directly into electrical energy. In this article, we explore the fascinating science behind solar cells, how they work, and the different types of solar systems that bring solar power to homes and businesses worldwide.
We receive light and heat from the sun. Light provides us with vision and helps plants grow, which in turn supplies food, and heat helps us survive. The most interesting part is that by harnessing this light and heat, we can generate electricity.
Solar Cell
A solar cell is an electronic device that directly converts solar energy into electrical energy. Another name for a solar cell is Photovoltaic (PV) cell or PV.
In this context, ‘photo’ refers to light, and ‘voltaic’ refers to electricity. A collection of many cells together forms what is called a solar panel. Each cell is connected to one another. These solar cells function similarly to batteries. While a battery generates electricity from chemicals, a solar cell produces electricity from light.
Photovoltaic cells are made from a semiconductor material called silicon. When sunlight falls on the cell, some of the energy from the light is absorbed by the photovoltaic cell, allowing it to flow through the semiconductor material. This energy separates the electrons, allowing them to move freely.
We know that the smallest particle of light is called a photon. This means that the sun is showering billions of photons around us. If these photons are directed onto a photovoltaic cell, each cell will produce a small voltage of electricity. When the voltages of many cells in a panel are combined, they produce enough voltage to power devices.
Solar Power System
The purpose of a solar system is to generate electricity from sunlight. This method generally comes in two forms:
- On-grid Solar System
- Off-grid Solar System
On-grid System
An on-grid system operates without a battery as long as there is sunlight.
Equipment required for an on-grid system:
- Solar panel
- On-grid inverter
- Energy meter
Off-grid System
An off-grid system stores solar electricity in batteries for use at night or during power outages.
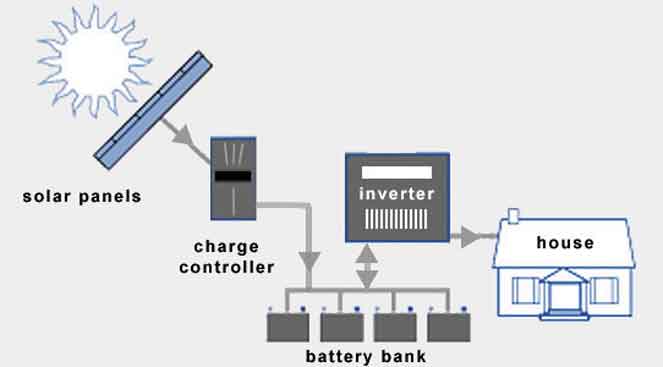
Equipment required for an off-grid solar system:
- Solar panel
- A charge controller
- An inverter
- Battery bank
Solar Panel
A solar panel is a device used to generate electricity. The electricity produced is typically DC (Direct Current). Various quality solar panels are available in the market.
Charge Controller
This device controls the battery’s charge. When the battery is fully charged, it stops charging. Similarly, when the battery is discharged, it disconnects the load, protecting the battery.
Inverter
We know that the electricity produced by a solar panel is typically DC. This DC power is stored in the battery bank via the charge controller. However, most household appliances use AC (Alternating Current), so the DC power needs to be converted to AC, which can be done using an inverter.
Battery Bank
A battery bank is a collection of multiple batteries. These batteries can be connected in series or parallel. To increase voltage, the batteries are connected in series, and to increase current, they are connected in parallel.
Specifications of a Solar Panel
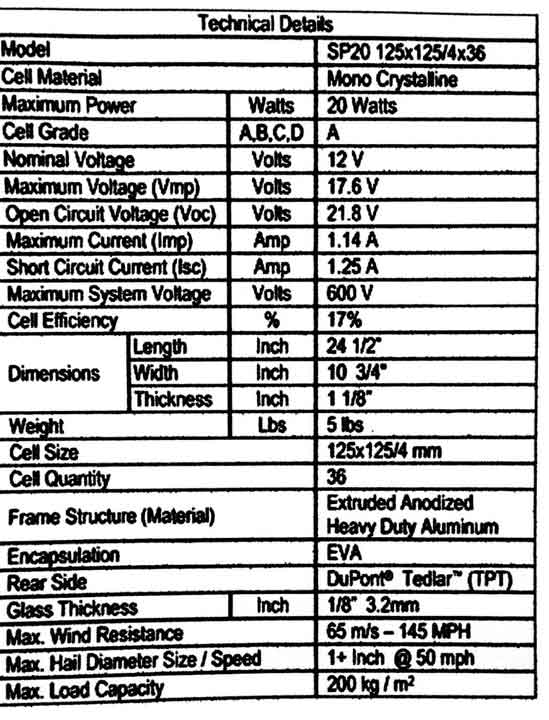
1. Maximum Power: This means the solar panel can produce a maximum of 20 watts of electricity.
2. Maximum Voltage: The maximum voltage of the panel is 17.6 volts.
3. Open Circuit Voltage (Voc): The voltage measured when there is no load on the solar panel is referred to as Voc.
4. Maximum Current: This refers to the maximum current the panel can provide. Ensure that no load is connected that requires more current than the panel can provide.
5. Short Circuit Current: This is the current that flows during a short circuit in the system.
6. Maximum System Voltage: When solar panels are connected in series, ensure that the voltage does not exceed the maximum system voltage. Here, the maximum voltage is 600 volts, meaning (600/17) = 35 panels can be connected in series.
FAQ: Solar Power Systems
What is a solar power system?
A solar power system is a setup that converts sunlight into electricity using solar panels. It can be used for residential, commercial, or industrial purposes to generate renewable energy.
What are the 3 types of solar power systems?
On-grid systems: Connected to the utility grid, allowing excess power to be sent back.
Off-grid systems: Independent of the grid, storing energy in batteries for later use.
Hybrid systems: A combination of both, using solar energy with battery storage and grid backup.
How does a solar power system with battery work?
A solar power system with a battery stores excess energy produced by solar panels. This stored energy can be used when sunlight is not available, such as during the night or cloudy days, ensuring continuous power supply.
How to use a solar system?
A solar system is used by installing solar panels on a roof or open space to capture sunlight. The panels convert sunlight into electricity, which is then used to power appliances and devices in your home or business.
How do solar power systems work?
Solar power systems work by capturing sunlight with solar panels, converting it into direct current (DC) electricity, which is then transformed into alternating current (AC) electricity by an inverter to power homes or businesses.
Which type of solar system is best?
The best type of solar system depends on your energy needs. On-grid systems are ideal for locations with reliable utility connections, while off-grid systems are suitable for remote areas. Hybrid systems provide flexibility with both solar and grid power options.
What are the advantages of solar energy?
Reduces electricity bills
Environmentally friendly and renewable
Low maintenance costs
Increases property value
Provides energy independence
What is a solar power plant?
A solar power plant is a large-scale installation of solar panels that generates electricity for commercial or industrial use, or to supply energy to the grid. It usually covers extensive land areas and produces high output compared to residential systems.
Read More: