A fuse is an essential electrical safety device designed to protect circuits from excessive current flow. By using a thin, low-melting-point conductor, a fuse can disconnect a circuit when the current exceeds a safe level, preventing potential damage or hazards. In this article, we will explore the function of fuses, how they operate, the materials used in fuse wires, and both the advantages and limitations of using fuses in electrical systems.
What is a Fuse?
A fuse is a short, thin conductor with a low melting point that is capable of carrying a specific amount of current indefinitely when connected to an electrical circuit. If more current flows than the specified limit, the fuse melts, disconnecting the faulty section of the circuit from the source.
Thus, it can be said that a fuse is an electrical safety device.
How Does a Fuse Work?
The function of the fuse wire is to carry a specific amount of current (normal current) without generating excessive heat. When excessive current flows in the circuit, the fuse wire begins its operation.
A fuse contains a piece of metal wire. When excessive current flows through the circuit, this metal wire melts, protecting the circuit. After the fuse operates, it can be easily reused by replacing the metal wire.
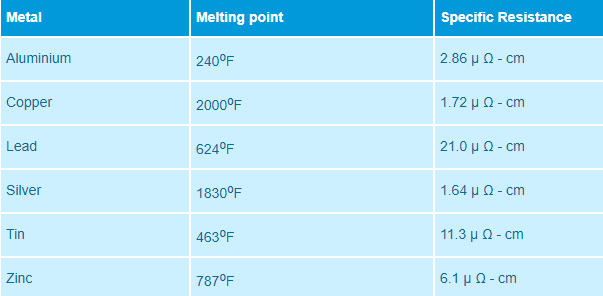
Materials Used for Fuse Wires
- Tin
- Lead
- Zinc
- Silver
- Antimony
- Copper
- Aluminum, etc.
What is Fusing Current?
We know that when excessive current flows through a fuse, its wire melts. The minimum current at which the fuse wire melts is called the fusing current. This current is higher than the current rating of the fusing element.
What is the Cut-Off Current of a Fuse?
The cut-off current of a fuse is the maximum current the fuse can handle before its wire melts due to a short circuit.
What is the Current Rating of a Fusing Element?
When excessive current flows through the fuse wire, it becomes very hot. The maximum amount of current the fuse wire can carry without melting in this overheated state is called the current rating of the fuse.
What is the Fusing Factor?
The ratio between the minimum fusing current and the current rating of a fuse is called the fusing factor.
Therefore, Fusing Factor = Minimum Fusing Current / Current Rating of the Fuse Element.
The value of this ratio is always greater than 1.
Advantages of Fuses
- A fuse is the simplest and easiest protective device.
- It requires no maintenance.
- Its operating time is shorter compared to a circuit breaker.
- The fuse wire can be replaced as needed.
- It is cost-effective.
- It is well-suited for overcurrent protection.
- It interrupts short circuit current without noise, smoke, or gas.
Disadvantages of Fuses
- It is difficult to accurately determine the specific rating, so sometimes the fuse does not blow at the right moment.
- The fuse wire should not be too thick. Many people unknowingly use thick wire, preventing the fuse from melting during a short circuit.
- Due to its cut-off effect, high voltage reactive circuits can generate significant induced voltage.
- It lacks arc extinguishing capability, making it unsuitable for use in high voltage lines above 33kV.
What is the short answer of fuse?
A fuse is a safety device that protects electrical circuits from excessive current by melting and breaking the circuit when the current exceeds a set limit.
What is the function of a fuse?
The main function of a fuse is to safeguard electrical circuits by disconnecting them when the current surpasses a safe threshold, preventing overheating or damage.
What are fuses used for?
Fuses are used to protect electrical devices and systems from short circuits, overloads, and potential fire hazards caused by excessive current flow.
What is fuse and types?
A fuse is a protective device that melts to break a circuit during excessive current flow. Common types of fuses include cartridge fuses, blade fuses, and resettable fuses.
Where is fuse used?
Fuses are used in various applications, including household appliances, automobiles, industrial machinery, and electrical distribution systems.
Why is fuse needed?
Fuses are necessary to prevent damage to electrical devices and wiring caused by overcurrent, which could otherwise lead to equipment failure, fires, or safety hazards.
What is the principle of a fuse?
The principle of a fuse is to melt and break the circuit when the electrical current exceeds a specific value, stopping the flow of current and protecting the system.
What is the advantage of fuse?
The advantage of a fuse is its simplicity, affordability, and reliability in protecting electrical circuits from overloads or short circuits.
What are simple fuses?
Simple fuses consist of a metal wire or strip that melts when the current exceeds a specific value, effectively interrupting the circuit to prevent damage.
Read more: What is drop out fuse?